Post Cardiac Arrest Myoclonus - Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from.
Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of.
Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor.
JCM Free FullText PostCardiac Arrest Mechanisms, Management, and
Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the.
Postcardiac arrest brain injury manifests as coma, seizures, myoclonus
Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the.
Healthcare Free FullText PostHypoxic Myoclonus Status following
Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on.
Neuroprognostication after cardiac arrest EMCrit Project
Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been.
Figure 1 from Characteristics of Cardiac Arrest Survivors With
Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web myoclonus, the.
Table 1 from Neurologic recovery after therapeutic hypothermia in
Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence.
1 Time course of cardiac arrestinduced posthypoxic myoclonus in rats
Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the.
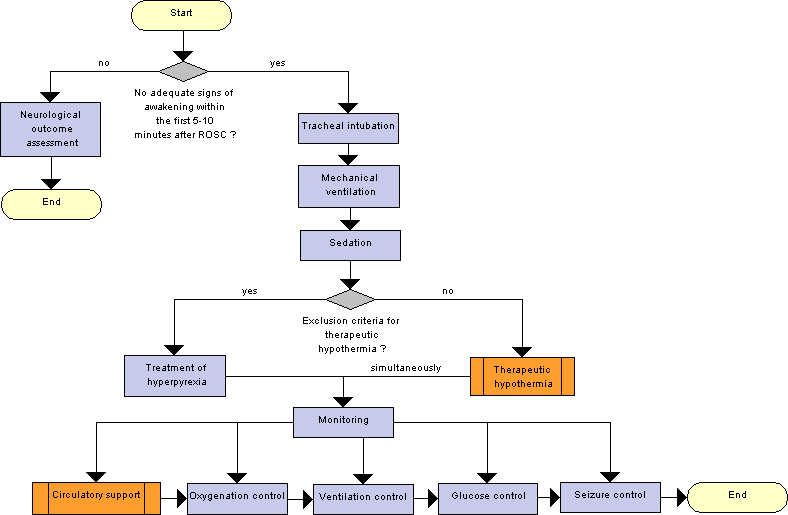
Flow diagram of post‐cardiac arrest patient evaluation. Abbreviations
Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web myoclonus, the.
Figure 1 from Guideline for resuscitation in cardiac arrest after
Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac.
Infographic on the difference between heart failure and a heart attack
Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor. Web myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often.
Web Myoclonus, The Brief Involuntary Twitching Of A Muscle Or Group Of Muscles, Occurs In About 20% Of Patients Resuscitated From.
Web myoclonus emerges later after the occurrence of cardiac arrest, often after several days. Prognostication after cardiac arrest often depends primarily on neurological function, and characterizing the extent of. Web diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest. Web the presence of early posthypoxic myoclonus (phm) following cardiac arrest had been invariably associated with poor.